In recent years the geopolitical situation in the world has brought to a head. This affects the whole world and has the influence on the development of many countries, on the economic and political relationships between them. So, this is an important issue for the consideration and it is critical to analyze the possible risks and the consequences for the Russian economy.
According to the review of the International Monetary Fund in June 2014, the pace of growth of the Russian economy remained slow in 2013 due to the pre-existing structural problems. In 2014 it was complemented by the geopolitical tensions in the relations with Ukraine [1].
Of course, all we know that the geopolitical risks include such elements as the risk of the external conquest, the risk of the collapse of the state under the internal forces influence, the risk of the sovereignty reduction, the political risk, the country risk and so on.
Now, the geopolitical risks are clouding the future of the Russian economy. First of all, the uncertainties are expected to hinder the economic growth in the short and medium terms. The restrictions, related to the production capacity, continue to constrain the economic growth. It is also should be mentioned, that the continuing geopolitical uncertainties are likely to affect the attraction of the investments.
It’s common knowledge that the many countries and the EU reacted to the situation in Ukraine by imposing the sanctions against the Russian legal entities and individuals.
The main consequences of the sanctions for Russia were the increase of the perceived risk of doing business in Russia, which has had a deterrent effect on the investments and the strong pressure on the Ruble. However, it should be noticed, that according to the Doing Business Ranking the Russian Federation takes the 51 place and in comparison with the previous years this indicator has risen [2]. This fact can attract the investors to do business in Russia.
In these conditions the Central Bank of Russia undertook the key several actions, which were the following:
- The increase of the interest rates
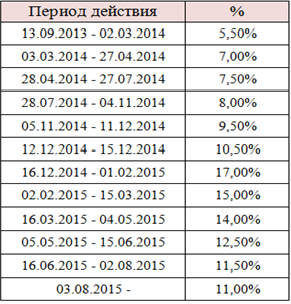
- The elevation of the key rate since 5,5% in 2013 till 17% in 2015 [3] (see table 1)
- The moderately tight monetary policy
- The usage of the foreign exchange reserves to support the Ruble
Table 1 – «Central Bank of Russia key rate changes»
Source: CB of Russia statistical bulletin №3, 2016
Moreover, the prospects for economic growth in Russia are connected with the changes in the oil prices and the factors of the capacity utilization and the labor force growth, but these factors will be expected to constrain the growth in the future.
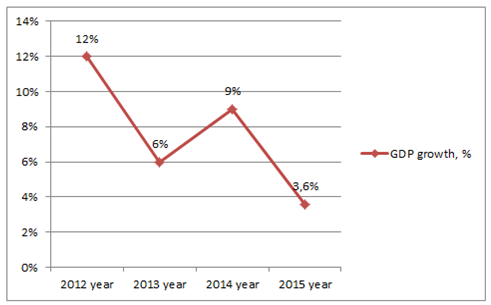
The Russia’s economic growth has been slowing since 2012. For instance, you can see on the graph below of the GDP growth in current prices, that this indicator shows the lower growth from year to year. In 2012 the growth rate had been 12%, in 2013 this figure fell twice, in 2014 this indicator reached 9% and in 2015 dropped to 3,6% due to weakening the domestic demand amid rising the geopolitical tension [4].
Picture 1. Russia’s GDP growth since 2012 till 2015
Source: CB of Russia statistics of GDP
It is important to understand, that the consequences of the geopolitical risks, the introduction of the sanctions against Russia and the retortion can affect not only the development of Russia, but also the development of other countries (in a positive or negative way), which can include the Russia’s partners too.
So, which countries may suffer from the slowdown in the Russian economy? First of all, they are the neighboring countries, which have the significant ties with Russia through the trade (Belarus, Lithuania, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine and Estonia), the financial sector (through the foreign direct investments) (Cyprus, Luxembourg, the Bahamas, Saint Kitts and Nevis and the Seychelles) and the remittances (Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova and Tajikistan). These countries may incur losses in the wake of the Russia’s recession.
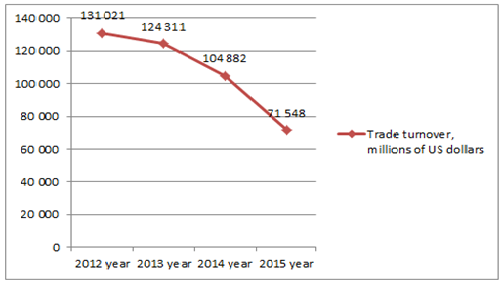
Really, the trade turnover between Russia and the CIS countries has gone down since 2012 year. In 2015 this indicator reached 71 548 millions of US dollars (see picture 2) [5].
Picture 2. Trade turnover between Russia and the CIS countries since 2012 till 2015 years
Source: CB of Russia statistics of internal trade
One of the main important points is the fact, that the events in Ukraine may also disrupt the export of oil and gas from Russia. For example, the Baltic States, Belarus, Finland and the Czech Republic almost completely satisfy the domestic demand at the expense of the Russian gas. The level of the dependence is also high (40-60 per cent) in the Central and South-Eastern Europe. In these countries, the disruptions in the gas exports from Russia could have the significant implications for the economy.
It’s very important to be said that the influence of the “geopolitical risks” gradually begins to transform into the real figures of the macroeconomic statistics. The IMF had lowered its forecast for the global economic growth in 2014 from 3.7% to 3.4%, which, given the development of the sanctions war and the inevitable bankruptcy of Ukraine, had looked overoptimistic.
And of course it cannot be overlooked that of the major economies, only China today shows the growth rates above the global outlook, and these rates are well below the usual growth in China.
It is necessary to pay the attention to «The paradox of the global financial markets». It consists of the fact that the financial markets of distressed states affected, for instance the Russian currency, stock and bond markets, but the overall detrimental effect, which is usually created by the geopolitical conflicts, is not materialized.
The world financial markets did not react for several reasons, let’s consider them:
- Firstly, the central banks of the developed countries (US, EU, UK and Japan) continue to keep the key interest rates near zero, and the long-term interest rates remain at a low value. This pushes up the prices of the risky assets.
- Secondly, investors have taken the note that the conflict between Russia and Ukraine remains limited and won’t develop into a full-scale war.
Thus, there are reasons for the mild reaction of the global markets to the geopolitical risks.
Of course, it cannot be excluded that the situation can change. There are few scenarios of the situation development. Firstly, the markets can be wrong in the fact that the conflict between Russia and Ukraine do not extend or intensify. The international policy of Vladimir Putin may become more aggressive. Secondly, the geopolitical conflicts can launch a global infection, when and if there is a systematic factor.
In conclusion I’d like to stress that although the global financial markets remain calm, the collapse of the financial system cannot be excluded. A century ago the financial markets laid the very low probability of the occurrence of a serious conflict, blindly ignoring the risks that led to the First World War. Such risks still exist today.
References
- Geopolitical risks cloud future of Russian economy // IMF Survey Magazine. June 30, 2014. URL: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/survey/so/2014/car063014a.htm.
- Doing Business 2016: Measuring Regulatory Quality and Efficiency. Washington, DC: World Bank. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: http://www.doingbusiness.org/~/media/GIAWB/Doing%20Business/Documents/Annual-Reports/English/DB16-Full-Report.pdf.
- Статистический бюллетень Банка России // Банк России. – 2016. – №3. – 308 с. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: http://www.cbr.ru/publ/BBS/Bbs1603r.pdf.
- Статистика Банка России – Валовый внутренний продукт в текущих ценах // ЦБ РФ. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: http://www.gks.ru/free_doc/new_site/vvp/vvp-god/tab1.htm.
- Статистика Банка России – Внешняя торговля Российской Федерации товарами // ЦБ РФ. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/default.aspx?Prtid=svs&ch=vt#CheckedItem.

 View this article in Russian
View this article in Russian